Introduction to GitHub and Open Source Collaboration#
GitHub is one of many social coding platforms that allows individuals and teams to manage, track, and collaborate on software projects. Social coding platforms play a key role in open source development, enabling contributors worldwide to work on, improve, and maintain code and documentation together.
This guide covers: The social aspects of contributing to an open source project
How to get started contributing to open source
The technical aspects of contributing including:
What GitHub is and how it supports open source communities
Why contribute to open source?#
Contributing to open source is a way to build skills, expand your network, and give back to projects you care about.
Improve your skills: Gain hands-on experience with real-world projects.
Grow your network: Connect with developers, maintainers, and potential collaborators.
Showcase your work: Contributions become part of your public portfolio.
Support tools you use: Many contributors improve projects they rely on for work or hobbies.
Learn from others: See how experienced developers write and manage code.
Social cue: Open source is collaborative—every contribution, big or small, helps the community.
Open source and academia
Academia heavily values publications for career advancement, yet open source contributions are often not recognized and valued in traditional academic credit systems despite being essential to scientific progress. pyOpenSci is an organization committed to helping scientists get support and recognition for their important work in developing and supporting open source through peer review and its vibrant and supportive community of practice.
Using GitHub for personal projects#
Many people start using GitHub as a personal version control tool. This means tracking changes to your own work without collaborating with others.
Solo workflow#
Clone a repository: Copy the project to your local computer.
Work locally: Edit files and make changes.
Commit changes: Save changes with a description of what was modified.
Push changes: Upload updates to GitHub as a backup.
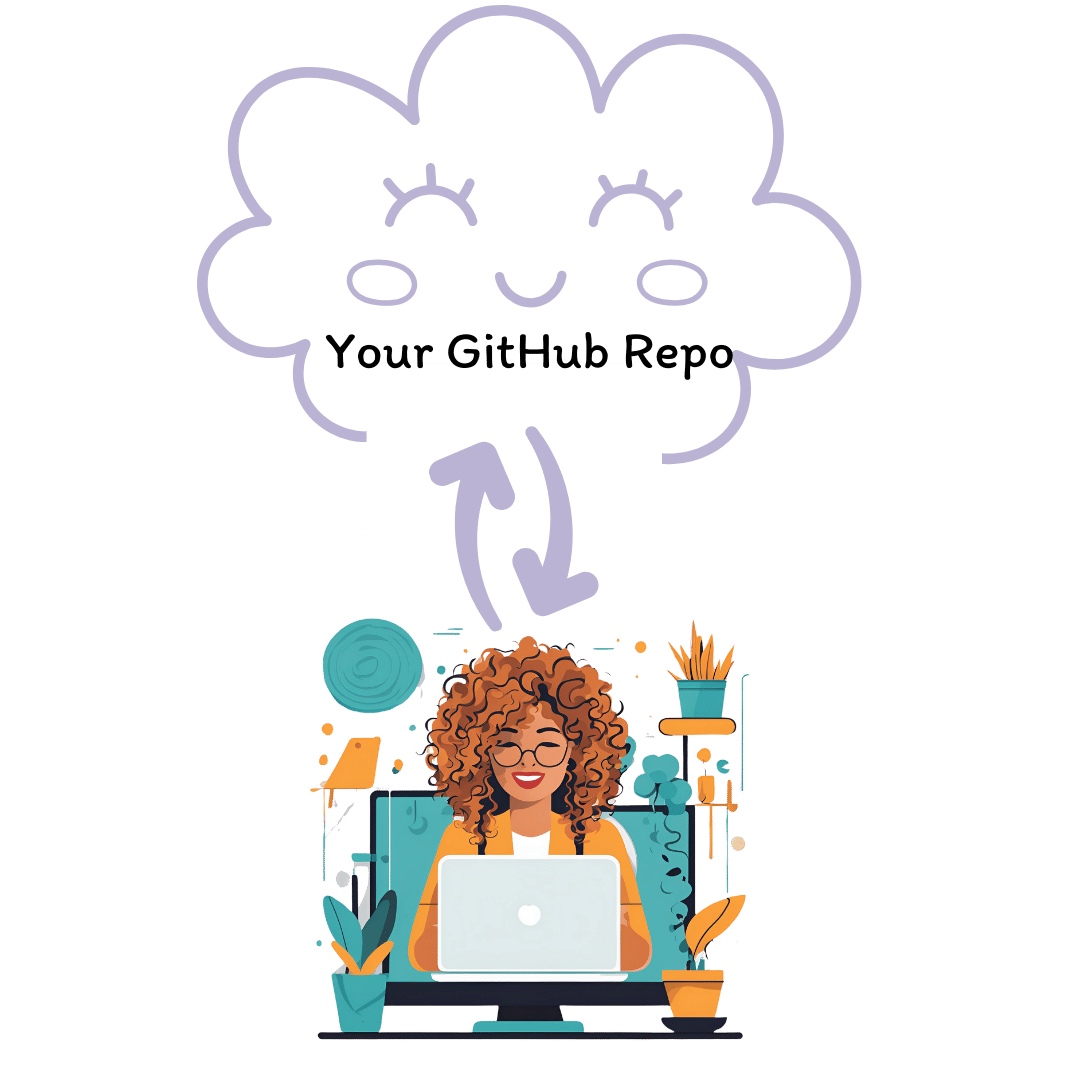
Social cue: GitHub is useful even when working alone. It creates a backup of your work and allows you to track changes over time—helpful for research, coding, or writing.
Using GitHub collaboratively#
GitHub is widely used in open source and team-based projects where multiple people work on the same codebase.
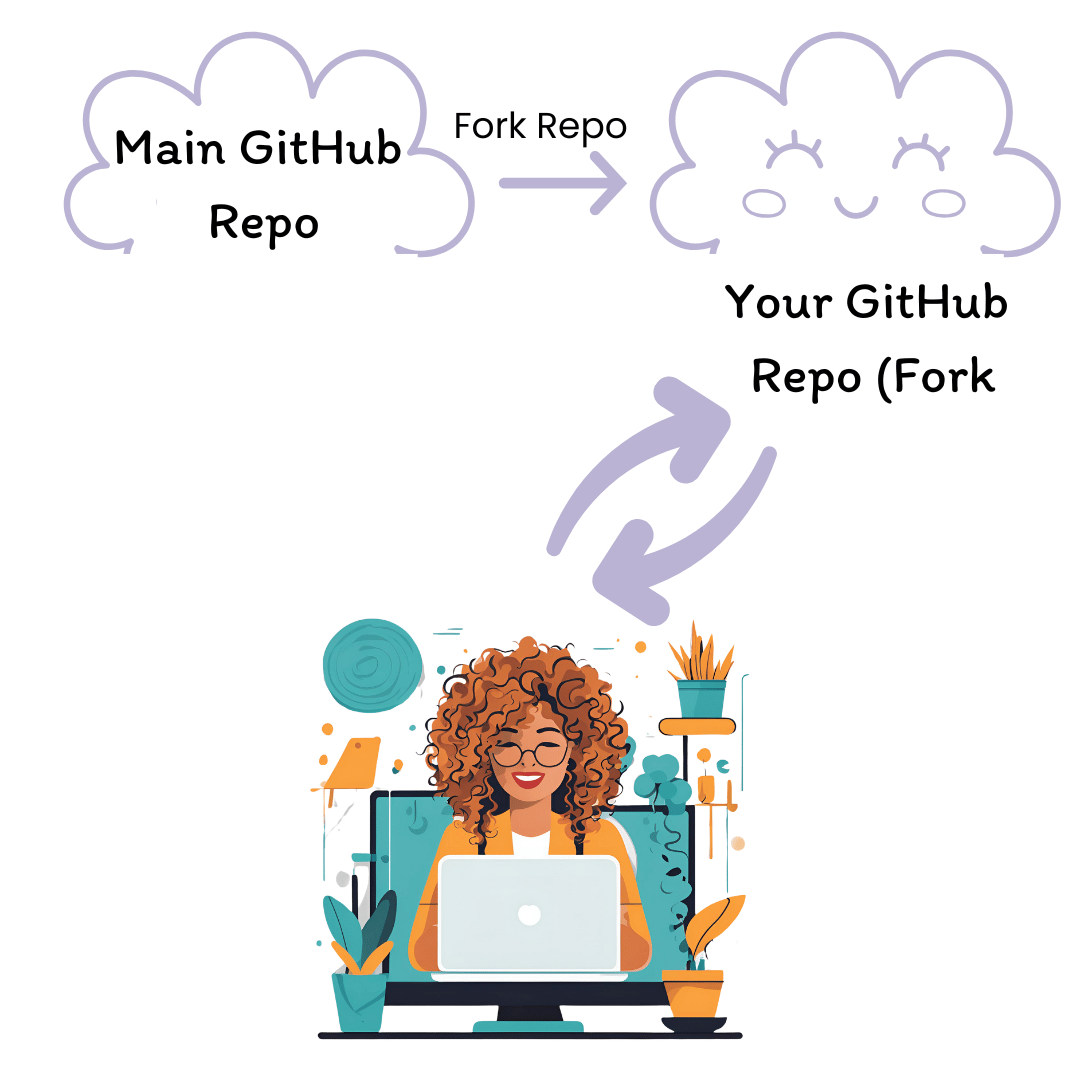
Collaborative workflow#
Fork a repository: Create your own copy of the project on GitHub.
Clone locally: Download your fork to work on it.
Make and commit changes: Edit files and save your changes.
Push to your fork: Upload updates to your GitHub copy.
Open a pull request: Suggest changes to the main project.
Collaborate and merge: Review and integrate updates.
Key difference: Instead of pushing changes directly to the project, you first fork it and work within your own copy before submitting a pull request to propose changes.
Social cue: Working on GitHub is more than writing code—it’s about communication, teamwork, and reviewing each other’s work.
Summary#
Feature |
Solo Use |
Collaborative Use |
|
|---|---|---|---|
Main goal |
Personal version control |
Team-based development |
|
Repository type |
Single personal repo |
Forked repositories linked together |
|
Workflow steps |
Clone, edit, commit, push |
Fork, branch, pull request, merge |
|
Review process |
Self-review changes |
Maintainers review contributions |
What’s next?
Now that you understand GitHub’s role in open source and collaboration, you’re ready to dive into contributing to a project!
This work was supported by the Better Scientific Software Fellowship Program, a collaborative effort of the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE), Office of Advanced Scientific Research via ANL under Contract DE-AC02-06CH11357 and the National Nuclear Security Administration Advanced Simulation and Computing Program via LLNL under Contract DE-AC52-07NA27344; and by the National Science Foundation (NSF) via SHI under Grant No. 2327079.


Social coding platforms and open source#
Open source software (OSS) is code that is publicly accessible—anyone can view, modify, and distribute it. GitHub provides the tools needed for open source projects to store code publically, manage contributions, track and address issues, and collaborate efficiently.
Specifically, in the Python language, the software is often associated with Python packages, where you bundle up code and make it easier for a user to install on their computer. Reusable software allows developers and scientists to share common workflows rather than needing to recreate the code needed for each workflow from scratch.
Why open source communities use GitHub#
Global collaboration: Developers from around the world can contribute.
Version control: Track every change made to the project.
Transparent discussions: Use issues and pull requests to propose and review changes.
Permission control: Maintainers decide what contributions get merged.